Applying face masks is a very popular skincare technique. Face masks have significant benefits for skin maintenance and care, especially when the skin is dehydrated, as they can provide a substantial amount of moisture absorption.
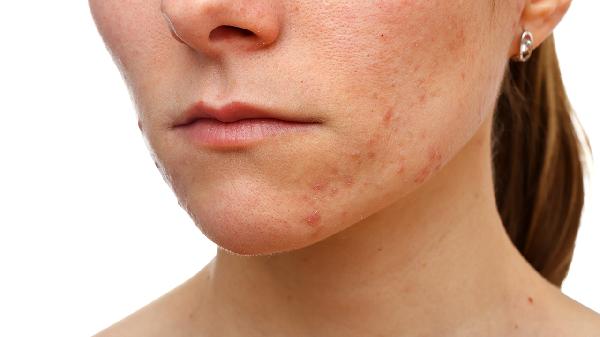
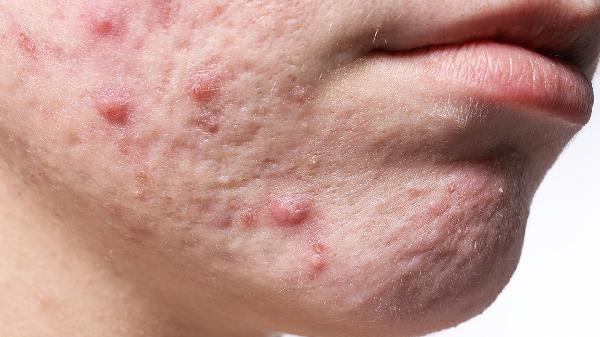
Getting acne after using hydrating masks.
Acne after applying face masks can be related to skin allergies, overuse of masks, or leaving the mask on for too long. These issues may require medical treatment.
1. Skin allergies: There are many types of masks on the market, but not every hydrating mask suits everyone. Some masks contain complex ingredients that can cause skin allergies, leading to acne breakouts. If you experience itching or swelling after applying a mask, remove it immediately and clean off the essence from your face.
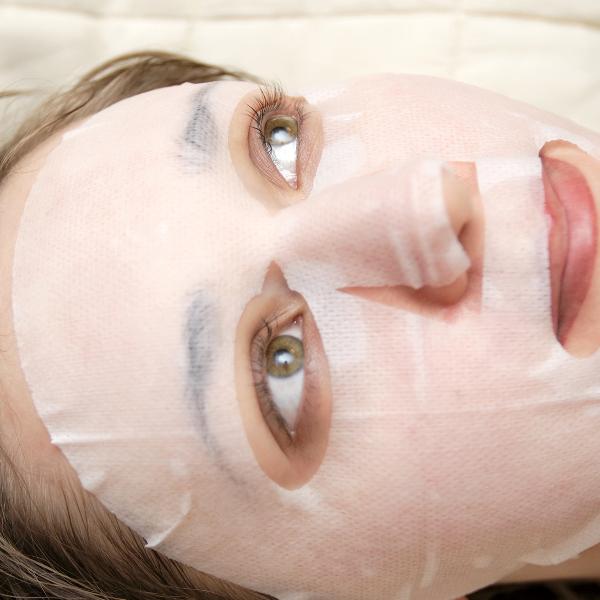

2. Overuse of masks: Applying masks too frequently, such as daily, can damage the skin barrier, thin the stratum corneum, and make the skin more sensitive. It's recommended to use masks three to four times a week.
3. Prolonged use of masks: While some overnight masks can be left on, most hydrating masks shouldn't be used for too long. Typically, a sheet mask should be worn for about 15-30 minutes. Prolonged use can affect normal skincare routines and skin health. Acne has its reasons, and it's essential to identify the cause and treat it accordingly to improve acne-prone skin and restore skin smoothness.
Why do I get acne after using face masks?
1. Consider if your facial skin is allergic.
If acne is caused by using masks, consider if your facial skin is allergic. Sensitive skin is prone to allergies, so it's crucial to know your skin type. If you have sensitive skin, test the mask essence on your ear before applying it to your face. If redness occurs, avoid using that mask.
2. Using unsuitable hydrating masks can also cause acne.
For many people, using unsuitable masks can lead to acne. Unsuitable masks may have unfavorable ingredients or materials. Always check the ingredients before purchasing. Ingredients like salicylic acid or amino acids are generally beneficial, but some people may be allergic to them. The mask's material also matters; some are made of cotton, others of silk, which some may be allergic to.
3. Don't wear masks for too long.
Control the duration of mask application. Prolonged use can cause allergies, leading to acne. It's recommended to wear masks for about 20 minutes. Overuse can burden the skin, so limit mask use to two or three times a week.
4. Always rinse your face with water after using a mask.
If you notice acne after using a mask, rinse your face with water. Not all mask essences are beneficial; they can make your skin sticky and hinder skincare.
5. Focus on skincare.
Skincare is crucial. Even if you're short on time, using hydrating sprays can benefit your skin significantly.
Do I need to wash my face before applying a mask in the morning?
Yes, washing your face before applying a mask in the morning is essential for better product absorption. Morning masks enhance makeup application, and hydration masks are typically used. Evening masks are more effective; two to three times a week is sufficient. Start by cleansing your face with a cleanser, apply toner, then place a hydrating mask on your face. The best time for a morning mask is between six to seven AM, with 15 to 20 minutes duration. After mask application, clean your face, proceed with daily skincare, and then apply makeup for a smoother finish and to avoid dullness.
Hydrating mask's moisturizing principle.
Hydrating masks temporarily isolate the skin from air and pollution, allowing pores to expand and moisture from the mask to penetrate the stratum corneum, supplementing water to the skin, making it soft and elastic. Skin has three layers: epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. Epidermal cells contain moisturizing components that absorb environmental moisture, protecting and hydrating the skin. Hydrating masks work on this layer. There are many types, with varying effects, but basic hydration is consistent. Prolonged exposure to UV and air unavoidably damages the skin, causing dryness and fine cracks. Immediate hydration activates skin cell growth, repairing damaged skin. Masks temporarily isolate skin from air, surrounding it with essence, softening the stratum corneum, and moisturizing the skin. Face temperature slightly increases during mask application, expanding pores for easier debris removal, cleaning the skin effectively. The stratum corneum absorbs moisture from the mask, swelling and making the skin appear fuller. Light reflects more uniformly, making the skin look brighter and more even.