Sexually transmitted diseases, also known as "venereal diseases," traditionally refer to diseases transmitted through sexual intercourse, primarily affecting the genital area. They include syphilis, gonorrhea, chancroid, lymphogranuloma venereum, and granuloma inguinale, which were once referred to as "social diseases." Currently, over 20 types of sexually transmitted diseases are recognized internationally, including the traditional five venereal diseases, as well as non-gonococcal urethritis, genital warts, genital herpes, AIDS, bacterial vaginosis, vulvovaginal candidiasis, trichomoniasis, scabies, pubic lice, and hepatitis B. In China, the eight key sexually transmitted diseases currently targeted for prevention and control are syphilis, gonorrhea, chancroid, lymphogranuloma venereum, chlamydia trachomatis infection, genital warts, genital herpes, and AIDS.
The symptoms of various sexually transmitted diseases are as follows:
1. Gonorrhea – This is a bacterial disease that can infect the cervix, urethra, rectum, eyes, or throat and often coexists with chlamydia. Symptoms of gonorrhea include a burning or itching sensation during urination, or possibly no symptoms at all.
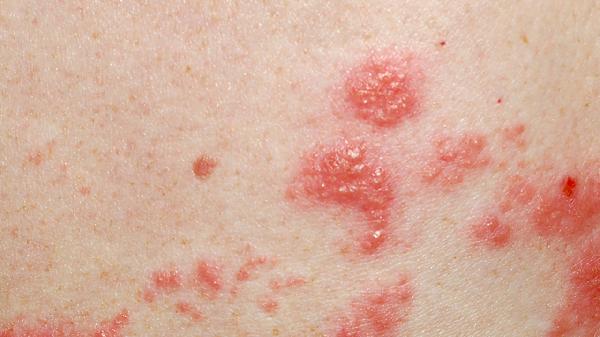
2. Genital herpes – Transmitted through skin contact. Symptoms start with itching or burning pain in the genital area, thighs, or buttocks. Subsequently, ulcers may appear on the genitals, buttocks, anus, or other parts of the body. These sores may heal within a few weeks, but for most people, the disease recurs. While herpes cannot be cured, it can be managed with antiviral medication, which can reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks. However, herpes during pregnancy can lead to serious complications. Genital herpes is caused by herpes simplex virus types I and II.
3. Chlamydia – This bacterial infection is currently the most common sexually transmitted disease and can be cured with antibiotics if treated early. 75% of women and 25% of men do not show symptoms. Symptoms include abnormal discharge, pain during urination, lower abdominal pain, or pain during intercourse.
4. Human papillomavirus – Also known as HPV or genital warts, is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections in the United States. As the name suggests, it is a virus, and once infected, the condition lasts a lifetime. Warts can appear on the vulva, inside the vagina, on the cervix, in the anus, or even in the throat.
5. Syphilis – This is caused by a bacterial infection that can affect the heart, eyes, brain, bones, and nervous system. Early syphilis presents as a painless ulcer on the genitals, usually appearing 10 days to 3 months after infection. Syphilis is a chronic sexually transmitted disease caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. It can invade the skin, mucous membranes, and various other organs.
The symptoms of various sexually transmitted diseases have been introduced. If you or a friend discover any of these symptoms, please seek medical examination and treatment promptly. Sexually transmitted diseases are highly contagious, and their harm cannot be ignored. Early detection and treatment are essential to avoid the distress of sexually transmitted diseases.
What are the common manifestations of sexually transmitted diseases in men?
1. Itching in the urethra:
This symptom in men is often considered an early sign of non-gonococcal urethritis or gonococcal urethritis.
2. Ulcers on the external genitalia:
If the ulcer is round, cartilage-like in hardness, painless, and single, it is often considered a chancre (syphilis); if the ulcer is soft, with jagged edges, shallow, painful, multiple, and with pus, it is often considered chancroid; if the ulcer evolves from clustered vesicles, soft and painful, it is often considered genital herpes.
3. Growths on the external genitalia:
If multiple infiltrative, gray-white, flat, raised papules or nodules are seen on the vulva or perianal area, easily eroded, and with a foul smell, they are often considered flat condylomas; if light red or gray-brown, cauliflower-like or cockscomb-like, pedunculated warts are seen on the vulva or perianal area, easily bleeding, they are often considered genital warts; if hemispherical papules the size of a grain of rice are seen on the perianal or vulvar area, with a central navel and waxy luster on the surface, and cheesy material can be extruded when the top is picked, consider molluscum contagiosum.
4. Generalized skin rash:
If generalized light red macules or dark red papules appear, painless and non-itchy, with the rash on the palms and soles, and desquamation around the rash on the palms and soles resembling a cuff, it is often considered secondary syphilitic rash.
5. Urethral discharge:
If purulent discharge appears at the urethral opening, thick, copious, and yellow, especially in the morning, it may be acute gonorrhea; if a transparent, sticky discharge appears at the urethral opening, in small amounts, it may be non-gonococcal urethritis.
6. Frequent urination, urgency, pain, and redness at the urethral opening:
If these symptoms appear in men, accompanied by painful nocturnal erections, it is often considered acute gonococcal urethritis.