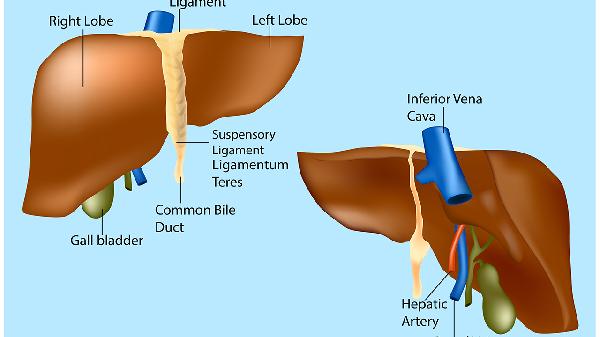
TCT检查是液基薄层细胞检测的简称,采用液基薄层细胞检测系统检测宫颈细胞并进行细胞学分类诊断,是目前国际上最先进的一种宫颈癌细胞学检查技术,TCT宫颈防癌细胞学检查对宫颈癌细胞的检出率几乎为100%,那么,如果进行TCT检查排除宫颈病变的同时,是否也能排除子宫内膜癌呢?宫颈癌和子宫内膜癌发病机制是不一样的,所以TCT检查宫颈癌阴性的情况下,并不能排除子宫内膜癌。子宫内膜癌有两种:雌激素依赖型和非雌激素依赖型。年轻患者往往是雌激素依赖型子宫内膜癌,和经常使用避孕药或者长期使用含雌激素的药物或保健品有关系,外源性雌激素过度增补会打破身体内激素的平衡,导致子宫内膜增生,如果出现不典型增生就容易进一步发展为子宫内膜癌。

TCT examination is the abbreviation of Thinprep Cytologic Test. It uses the Thinprep Cytologic Test system to detect cervical cells and perform cytological classification and diagnosis. It is currently the most advanced cervical cancer cytology examination technology internationally. The detection rate of cervical cancer cells by TCT cervical cancer prevention cytology examination is almost 100%. So, if a TCT examination is performed to exclude cervical lesions, can it also exclude endometrial cancer? The pathogenesis of cervical cancer and endometrial cancer is different, so a negative TCT result for cervical cancer does not rule out endometrial cancer. There are two types of endometrial cancer: estrogen-dependent and non-estrogen-dependent. Young patients often have estrogen-dependent endometrial cancer, which is related to the frequent use of contraceptives or long-term use of drugs or health products containing estrogen. Excessive exogenous estrogen supplementation can disrupt the hormonal balance in the body, leading to endometrial hyperplasia, and if atypical hyperplasia occurs, it can easily further develop into endometrial cancer.
再则,女性本身的肥胖、高血压、糖尿病等慢性疾病也可能会诱发癌变。肥胖人群中体内脂肪的芳香化酶作用下,可以使体内产生更多的雌激素,导致子宫内膜长期处于增生状态,容易发展为子宫内膜癌。此外,也有研究显示子宫内膜癌具有家族遗传性。子宫内膜的最终确诊依需要进行子宫内膜病理检查。只有当子宫内膜活检病理切片中发现癌细胞时,才能确诊为子宫内膜癌。宫颈TCT检查主要是在宫颈管部位取组织进行的一项检查,对于早期子宫内膜癌并没有较好的筛查作用,只能说,中晚期子宫内膜癌侵犯宫颈时,TCT检查才会发现。对于中老年女性,出现接触性出血、阴道不规则出血等情况下,需要进行宫腔镜检查和病理活检,排除子宫内膜癌存在的可能。
Moreover, chronic diseases such as obesity, hypertension, and diabetes in women may also induce cancer. In obese individuals, the action of aromatase in body fat can lead to increased production of estrogen, causing the endometrium to remain in a state of hyperplasia for a long time, which can easily develop into endometrial cancer. Additionally, studies have shown that endometrial cancer has a familial hereditary component. The definitive diagnosis of endometrial cancer relies on pathological examination of the endometrium. Only when cancer cells are found in the pathological biopsy of the endometrium can endometrial cancer be confirmed. The cervical TCT examination primarily involves taking tissue from the cervical canal and does not have a good screening effect for early endometrial cancer. It can only be said that when mid to late-stage endometrial cancer invades the cervix, the TCT examination may detect it. For middle-aged and elderly women experiencing symptoms such as contact bleeding or irregular vaginal bleeding, hysteroscopy and pathological biopsy are necessary to rule out the possibility of endometrial cancer.