Sexual Health
How to Diagnose Non-Gonococcal Urethritis: A Quick Guide
NGU, caused by pathogens like Chlamydia trachomatis, is an STD presenting with urethritis symptoms without gonococcal infection. Symptoms include urethral discomfort, discharge, and genital inflammation. Transmission can occur through sexual contact or childbirth, leading to complications like epididymitis or pelvic inflammatory disease. Diagnosis involves excluding gonorrhea and identifying specific pathogens through lab tests.
Diet Tips to Manage HIV and Prevent Progression
AIDS, a severe incurable disease, requires early virus suppression to reduce suffering. Key dietary principles include high-energy, high-protein foods, fresh vegetables, small frequent meals, and varied choices. Avoid spicy foods, maintain hygiene, exercise, and stay positive. Traditional remedies like bitter melon, kelp, garlic, soybeans, and cucumber may help inhibit HIV.
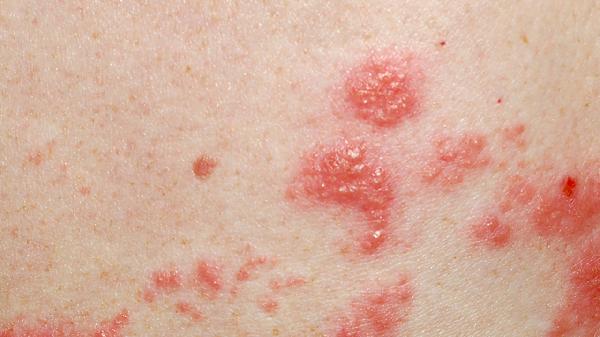
Syphilis' Devastating Impact on the Body Unveiled
Syphilis severely impacts physical and mental health, causing cardiovascular, skeletal, and nervous system damage, disability, and even death. It spreads through sexual contact, mother-to-child transmission, and contaminated items, with high infectivity and mortality. Prevention and timely treatment are crucial.
Top Ways to Test for HIV in the U.S.
HIV testing methods include blood, saliva, or urine samples, with blood being the most common. Key tests are ELISA, Western blot, and PCR. The window period, when antibodies are undetectable but the virus is present, is critical. Proper sample storage, transportation, and biosafety compliance are essential.
Top Tips to Prevent Genital Herpes Outbreaks
Genital herpes, a viral infection transmitted primarily through sexual contact, can be managed by avoiding unclean intercourse, maintaining hygiene during lesions, preventing colds, and abstaining from sex during treatment. Vaccines show promise but are not routine; ACV and condoms offer limited prevention.
What Causes Pseudocondyloma? Unraveling the Mystery
Pseudocondyloma acuminatum, a benign epidermal hyperplasia, is not sexually transmitted and often occurs in women aged 18-40. Its exact cause is unclear but may involve physiological variation, Candida presence, or chronic irritation. Symptoms include clustered papules, usually requiring no treatment but hygiene maintenance or laser therapy if necessary.
Early Signs of HIV: What You Need to Know
AIDS, caused by HIV, severely damages the immune system, leading to fatal infections and tumors. Transmitted via sexual contact, blood, or mother-to-child routes, HIV is fragile outside the body. Early symptoms include fever, rash, and lymphadenopathy. Testing during the 3-month window period is crucial for early detection.
Tackling Recurring Vaginitis: Effective Solutions and Prevention Tips
Hot weather increases vaginitis risk; 70% of women face reproductive health issues. Symptoms include discharge, itching, and odor. Seek medical advice, avoid self-medication, and maintain hygiene to prevent recurrence and complications.
Effective Care Tips for Tertiary Syphilis Patients
Tertiary syphilis, caused by mutated Treponema pallidum, increases disability and mortality risks. Treatment involves strict disinfection, tracking sexual partners, and preventive measures. Dietary remedies like dandelion porridge and plum flower porridge aid recovery, but medical treatment is essential. Avoid alcohol, tobacco, and spicy foods; focus on vitamin-rich options.
Four Key Approaches to HIV Treatment in the U.S.
HIV spreads mainly through sexual contact, blood transmission, and mother-to-child transfer. Sexual intercourse, especially unprotected anal and vaginal sex, is the primary route. Blood transmission occurs via contaminated needles, transfusions, or organ transplants. Infected mothers can pass HIV to their babies during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding. Prevention includes safe sex, sterilized medical tools, and antiretroviral therapy.